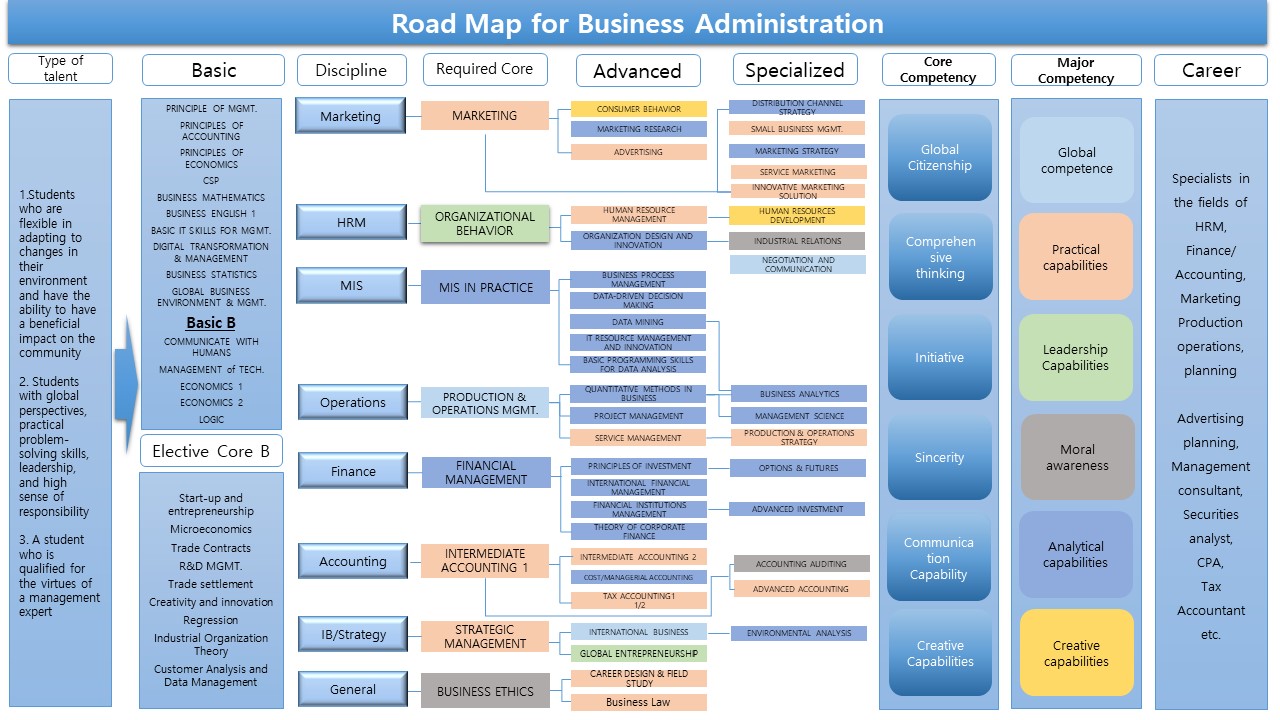
Road Map : Business Administration
Course Description
| Course Title | Course Description | Category | TEPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| MARKET REPORT | To actively cope with rapidly changing market conditions, companies must analyze markets and consumers in real time. Through this class, each student can analyze the current and future market conditions facing companies and develop detailed insight into micro and macro environments as well as the technology market environment. In addition, each student can learn the tools of comparative analysis between competitors through competitor analysis, internal competency analysis, and customer analysis. Needs of market report companies include micro analysis of products, customers, services, technology trends, proposals for collaboration with other divisions within a company, and business proposals for collaboration with strategic partners. Market reporting is very important as well as crucial to all corporate reports. In this course, students will learn how to prepare practical market reports for the businesses as well as develop important business skills to analyze the informational data of the market in order to prepare new business strategies, market strategies, marketing strategies, future strategies, etc. | Elective Core | '4-1 |
| INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS | This course provides an overview of the field of labor relations and examines the three major processes: union organizing (how labor unions are formed), bargaining (how union contracts are produced), and dispute resolution (how bargaining disputes and grievances are resolved). This course will help students to understand theoretical development regarding union roles, activities, and diverse consequences. It focuses on unions and their role in labor-management relations as well as the history of major labor unions, labor laws, and the general process of labor negotiations in a variety of work environments. To understand labor relations processes, this course first analyzes the framework in which collective bargaining takes place―the legal, historical, economic, and global environment, and alternative models of the employment relationship. Then, the latter part of this course examines international comparisons and important changes that have occurred. In order for students to gain a clearer understanding of labor relations, they will participate in mock contract negotiations and grievance resolutions. The focus of the course is private sector labor relations. However, public sector comparisons are highlighted where appropriate. | Elective Core | '4-2 |
| TECHNOLOGY AND INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT | High-technology product development strategy will be the one of the important issues for technology-oriented enterprises. For the successful launching and the positioning for their new product, marketers have to learn the entire process regarding high-technology new product development and production. To do that, each student should first learn about present and future technology trend analysis; secondly, research methodology on consumer behavior in the high-tech market; and thirdly, market success or failure case studies. This class enables each student's new idea generation to adapt to real high-tech markets so that innovative and creative high-tech new product strategy would be utilized as a high-tech marketer. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
| PRINCIPLE OF MANAGEMENT | This course introduces basic management principles and fundamentals of modern business administration. Fundamental management functions are examined from the viewpoint of cultivating managerial ability. Major topics include: essence of modern business administration, management planning and control, leadership and human resource management, basic principles of organizing, marketing management, operations management, financial management, and business unit management. In addition, this course covers a variety of issues related to venture management, knowledge management, and international management from the perspective of enhancing students' modern managerial concepts in the era of information society. | Basic | '1-1,2 |
| PROJECT MANAGEMENT | This course covers the various issues required for managing projects mainly from the managerial point of view. According to PMI'S PMBOK, project management is defined as “the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements". In this course, the following contents are covered: the concept of project management, project evaluation and selection, project planning and scheduling (CPM & PERT), project cost management, project control (EVM), resource constrained project scheduling, project organization management, project communication, and negotiation. | Elective Core | '4-1 |
| TAX ACCOUNTING2 | The objective of this course is to understand the process of calculating the taxable income of individual income tax and value added tax, and calculate the tax base and the calculated tax amount. Individual income tax studies the taxation structure of comprehensive income, capital gains, and retirement income. Comprehensive income includes interest income, dividend income, business income, earned income, other income and pension income. Students will be able to understand the process of determining type of each income. Capital gains tax is taught so that students will understand the scope and calculation structure of taxable capital gains. Other topics are: taxation, timing of supply, zero tax rate and exemptions, and tax payments. This course should enable students to understand tax issues of the scope, characteristics and types of taxation of simplified taxpayers. | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| GLOBAL BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT AND MANAGEMENT | Recently, globalization has made it critical for companies to understand the global business environment for effective business management. Hence, this course teaches students the elements of the global business environment and their implications for businesses. Specifically this course covers such elements of the global business environment as 1) world business environment, including international trade and investment, foreign exchange, economic integration, and international institutions; 2) country business environment, including political/economic/legal systems, national cultures, and technologies; and 3) market/industry business environment, including markets and industries. | Basic | '1-2 |
| MOT AND LEADERSHIP | The major actor of technology management is top management. Therefore leadership is very important in complex and dynamic changing economic and technological environments. Experts emphasize that the active involvement of top management is essential in successful management of technology. This course teaches the characteristics of MOT leaders and how to acquire and develop leadership in technology management. In addition, we will discuss several cases of successful MOT leadership. | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| DATA-DRIVEN DECISION MAKING | The goal of this course is to study effective decision making methods and theories based on data and related information technology, especially to understand emerging issues regarding big data. The following is a sample list of course subjects: -Strengths and limitations of data-driven decision making -Applications in HR, marketing, operations, etc. -Data warehouse and business intelligence -Business analytics -Big data decision making technology including visualization | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| VENTURE AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP | In this course, students will develop and derive global examples of entrepreneurship to study the ideas and challenging spirit of leaders who pioneered new markets. They will go through the process of discovering, searching, and exploring essential knowledge and practices to develop the skills necessary to start a business. Information and knowledge gathered while collaborating in teams will be shared with all students in the class. The learning competency applied in the new era is to transform into a market- and demand-driven dynamic thinking to foster creative and challenging talent that preemptively presents the direction in which a company should move forward. In this dynamic market, entrepreneurship is the key to breaking through difficulties. The students will think, analyze, discuss, and share ideas. | Elective Core | '2-1 |
| SPECIAL TOPICS IN BUSINESS | This course introduces the subject of recent changes in the business environment, new issues and cases of new markets in the fourth industrial revolution. Students will have a practical understanding of the key new technologies and business topics that have emerged during this era. They will sense the shifts that have occured in finance, services, health care, and manufacturing and predict expecting future trends. At the end of the semester, students can improve their ability to understand recent and new business trends and to draw solutions to the problems they face. With a vision of future trends, they can set the most appropriate career goals for themselves. | Elective Core | '4-2 |
| SERVICE MARKETING | The main objectives of this course are to develop an ability to evaluate, implement and lead effective marketing programs in service companies and organizations. Specifically, the course will center on providing students with the knowledge of how service marketing plays a key role in the success or failure of these organizations. This course will allow students to learn how to: -Analyze marketing and leadership problems of service driven companies and how they may or may not differ from product driven companies. -Develop plans to implement marketing programs in service companies that provide a supreme customer experience and extreme customer loyalty. -Understand the importance of segment and target research to service companies and how to find customers who value or need the service. -Negotiate, plan and implement integrated service marketing programs. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
| STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT | Strategic Management aims to help students to have an eye on the choice of firms' strategic direction and the general management of firms under high environmental turbulence. More specifically, Strategic Management is designed to educate students in the strategic management framework of environmental analysis, strategy formulation, strategy implementation, and strategy evaluation/control. In particular, it is designed to explore an organisation’s vision and mission, as well as examine principles, techniques and models of organisational and environmental analysis, and discuss the theory and practice of strategy formulation and implementation such as corporate governance and business ethics for the development of effective strategic leadership. | Required Core | '4-1,2 |
| FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS MANAGEMENT | Main topics of this course are theories and techniques for the management of financial institutions, emphasizing recent theoretical and empirical studies of relevant topics. We study the unique situations of Korean financial institutions. This course also provides students with an interest in financial institutions and financial markets through case studies for necessary basic knowledge. Students can develop and systematically implement principles of financial institutions. It is also important to understand a variety of information and knowledge in order to solve the problems of financial institutions. | Elective Core | '4-1 |
| SERVICE MANAGEMENT | Service Operations Management is a course which is designed to cover operational management issues in service organizations. Students are expected to study management issues related to service delivery and therefore, to understand how to improve service performance. Basically contents will be focused on service delivery systems, which is based on a customer-focused approach. But, for successful service business operational discussions such as process and resource management, service strategies, service concepts and service organizational culture and/or personnel issues will also be included. The course will deal with the basic knowledge of operational issues in service organizations, with frameworks and tools, through a variety of field cases. | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| BUSINESS PROCESS MANAGEMENT | This course provides the knowledge required to manage business process of an enterprise. The concept and definition of business process, how to construct business process architecture, notation to present and communicate business process, and techniques and methods to improve business processes. The course involves both an academic lecture and practical exercises to apply academic knowledge to real world problems. The main topics included in this class include: -Concept of business process -Business process architecture, and the concept of process hierarchy -Business Process Modeling and Notation 2.0 (BPMN 2.0) -Techniques and methods to improve business processes | Elective Core | '2-1 |
| INTERMIDIATE ACCOUNTING1 | Based on accounting principles, the course provides students with the necessary accounting concepts for understanding and generating financial information. This course is designed to educate students in accounting for assets, liabilities, and equity based on international financial reporting standards. | Required Core | '2-2 |
| PRINCIPLES OF INVESTMENT | Understanding of security investment, investment including utility theory, capital market, the effects of diversification, modern portfolio theory, option pricing theory, futures trade, and security analysis are the main topics in this course. Specifically, this course introduces various concepts and analysis tools to rationalize investments in financial assets from the perspective of institutional investors. These topics are based on the understanding of recent principles of domestic and foreign capital markets and financial instruments. In addition, mock investments are conducted in order to understand the concepts and analysis frameworks learned during lectures. | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING | This course's purpose is to provide an introduction and overview of accounting for managers in contemporary organizations. Whereas financial accounting focuses on providing information that is relevant and useful for external users, management (or managerial) accounting focuses on providing information that is relevant and useful for internal decision makers. Such information is used by managers in organizations (both profit and nonprofit) for strategic planning, evaluation and control. The topics of management accounting include cost behavior estimation, cost-volume-profit analysis, budgeting, standard cost and variance analysis, decision making, pricing decision, cost management, balanced score card, quality, throughput, management control systems and transfer pricing, etc. | Elective Core | '3-1,2 |
| STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT | Strategic Management aims to help students to have an eye on the choice of firms' strategic direction and the general management of firms under high environmental turbulence. More specifically, Strategic Management is designed to educate students in the strategic management framework of environmental analysis, strategy formulation, strategy implementation, and strategy evaluation/control. | Required Core | '4-1,2 |
| SMALL BUSINESS MANAGEMENT | This course analyzes the merits and demerits of small and medium-sized companies compared with large companies. Growth stage of small and medium-sized companies is illustrated. | Elective Core | '4-1 |
| MARKETING RESEARCH | The function which links the consumer, customer, and public to the marketer through information is analyzed. The main topics are the definition of problems, research design, questionnaires, research techniques, etc. | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| PRODUCTION & OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT | In every organization, managing activities of not only business production, but many other types of organizations such as hospitals, schools, public service, etc., understanding processes and/or systems in a scientific and systematic way is essential to effectively and efficiently make decisions. Issues of operations and/or positioning (system) strategy, demand forecasting, capacity planning, location, layout, scheduling, etc., including various innovative techniques and decision making models, are covered in this course. This course is one of the core business classes, so every business student is required to successfully complete this course. | Required Core | '2-1,2 |
| ADVERTISING | The complete advertising process from the objective setting to the effectiveness measurement of advertisement is illustrated through real cases. The main topics are message, media, creative strategy, copywriting, etc. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
| INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS | The importance of international management has been increased due to the development of information and communication technologies and the progress of globalization. The purpose of this course is to provide the theoretical and practical level of knowledge required to carry out business activities worldwide under such changes in the international management environment. Specifically, the emphasis is placed on cultivating the ability to make rational decisions on major issues of international management through a general understanding of (1) the global business environment, (2) the establishment and implementation of global strategies, and (3) the management of global enterprises. | Elective Core | '2-2 |
| ADVANCED ACCOUNTING | This course provides students with a thorough understanding of financial accounting theory and methodology employed by professional accountants. This course covers topics that were not dealt with in the intermediate accounting course previously offered. Topics covered in this course include business combinations, stock investments, consolidated financial statements, consolidation techniques and procedures, intercompany profit transactions, segment and interim financial reporting, derivatives and foreign currency, accounting for derivatives and hedging activities, and foreign currency financial statements. Prerequisite: Intermediate Accounting I & Intermediate Accounting II | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT | Financial decision-making in corporations and analytical techniques for solving financial problems are examined in this course. Financial decisions such as investing in fixed assets, obtaining debt and equity funds, and determining the proper amount of working capital are considered. Problems and cases are used to demonstrate the applicability of the analytical techniques. | Required Core | '3-2 |
| BUSINESS ETHICS | Today, business ethics are critical to achieving sustainable success. No enterprise will prosper or even survive while ignoring business ethics. With the domain and depth of business ever expanding in a globalized world, societal and public pressures on business ethics has been mounting incessantly. This course will expose students to typical ethical problems in complicated contexts and show how one can cope with them from practical yet multiple points of views. | Required Core | '4-1 |
| OPTIONS & FUTURES | This course covers derivatives and derivative markets such as futures, forwards, options and swaps. Specifically, it deals with the characteristics of derivatives, trading strategies using them, and valuation of derivatives. Further, we study speculative trading, arbitrage trading, hedge trading as a derivatives trading strategy, and important theories such as the Black-Scholes-Merton model and the binomial model. In addition, this course provides opportunities to simulate the KOSPI 200 Stock Index Futures and Options using the mock investment system, thereby understanding the trading environment for derivatives. | Elective Core | '4-2 |
| COST ACCOUNTING | This course is designed to provide an introduction and overview of cost information in contemporary organizations. Whereas financial accounting focuses on providing information that is relevant and useful for external users including investors, creditors, and governmental agencies, managerial (or management) accounting focuses on providing information that is relevant and useful for internal decision makers, i.e. managers. Cost accounting provides cost information for both financial accounting and managerial accounting. It measures, analyzes and reports information relating to the costs of acquiring or using resources in organizations. The topics of this course include job-costing, ABC, indirect cost allocation, process costing, spoilage, joint product costing, normal costing, standard costing, variable costing, etc. | Elective Core | '2-1,2 |
| CREATIVITY AND INNOVATION | Creativity and innovation are the key drivers of success in many industries today. They fuel the uptake of new technologies, the development of products and services and the formulation of strategies to secure competitive advantage. This course looks at how individuals and organizations use creativity and idea generation skills to identify and choose opportunities that enable innovation. Creative problem solving skills are developed and enhanced through a range of real world activities. An overview of idea generation tools is provided to help students understand problem solving. Ideas developed through these processes are then applied to a customer discovery approach to understand their value in the market place. | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| CAREER DESIGN & FIELD STUDY | This course is designed to provide early education on planning and development for students after graduation. It will provide a variety of opportunities for diagnosis and review of interests, values ??and abilities. It provides a way to set goals and develop future plans. It will help you to analyze your desired business type, job for employment, to improve your ability accordingly, and to make and implement a plan. Project results will be shared with the class. Project: Select the desired employment type, and job for each team, then study and present strategies to prepare for employment. Seek to understand the desired business type through mentoring with current seniors. | Elective Core | '3-1,2 |
| ACCOUNTING AUDITING | Auditing is the process of gathering and evaluating evidence (supporting documentation) for the purpose of reaching a conclusion regarding the fairness of reported financial information. In your accounting classes you learned how to apply various accounting rules. In this class, however, you will learn to determine whether or not a given organization has properly applied the necessary and appropriate accounting rules. In this course, you will become acquainted with a variety of important issues facing the auditing profession. Topics that will be covered include: necessity of the audit function, professional ethics as they relate to the audit profession, appropriate audit design, selected statistical sampling methodologies as they relate to auditing, auditor's responsibilities relative to an organization's financial statements, and auditing an organization's internal control systems. | Elective Core | '4-2 |
| MANAGEMENT SCIENCE | Management Science covers the formulation of mathematical and statistical models applied to decision making and the practical application of these models through the use of computers. Queueing models, computer simulation, and non-linear models are major topics. Learning scientific algorithms is important in the class; however, more attention is paid to the application of the tools to real management situations. In this course, other management science topics, such as project management, decision theory, and forecasting are also covered. Quantitative Methods in Business is a prerequisite. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
| PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING | The course will introduce students to accounting concepts and principles, and judgments and procedures that go into the preparation of corporate financial statements. The aim is to provide students with an understanding of assumptions and logic inherent in accounting techniques so that they become affective users of financial statements for decision making. Throughout the semester, there will be in-class discussions on the ethical considerations and implications of accounting choices made for financial reporting. Topics covered in this course include: the recording process, adjusting accounts, the accounting cycle, cccounting for merchandising operations, inventories, fraud, internal control, cash, accounting for receivables, plant assets, natural resources, intangible assets, current liabilities, non-current liabilities, investments, and statement of cash flows. | Basic | '1-1,2 |
| GLOBAL ENTREPRENEURSHIP(CAPSTONE DESIGN) | Global Entrepreneurship is designed to broaden students' knowledge in the field of international business and strategic entrepreneurship. The acquired skills and knowledge will enable students to develop a successful career in an international company or launch an individual enterprise domestically or abroad. The curriculum is developed on the basis of the combined international business experience of leading, globally-operating foreign and Russian companies. The course curriculum is practice-oriented and includes the participation of invited speakers from startup and leading companies. It consists of academic theories, business models, discussions, case studies, and projects. They enrich the academic process with specific examples and immerse students in the real business world. | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| EXPLORE TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT CASES IN ACTION | This course is designed to provide students with practical, case-based questions about the proper and active management of new technologies. Well-established business models at the global level have declined and failed, resulting in their replacement with new innovations. Therefore, students need to understand these trends in advance and learn how new innovations are reflected in corporate strategic decisions. Through this process, we learn from examples how different methods of innovation are actually implemented as processes and activities. In addition, we learn that technological development and business model innovation are strongly intertwined, and explore not only typical innovation categories, but also new types and methods of innovation that are difficult to reach through textbooks and how they evolve. There are no special prerequisites that are necessary for this course. Attendance and active participation in class are important, however, and it is essential to have basic competence in reading and understanding materials written in English. | Elective Core | '2-1 |
| BASIC IT SKILLS FOR MANAGEMENT | Students are to explore a suite of software tools (Excel, Access, Acrobat, PowerPoint, Word, and Google Docs) so that they can be well prepared for taking on financial and analytical problems as well as presenting and disseminating business ideas. | Basic | '1-1,2 |
| INNOVATION MANAGEMENT | Innovation, in principle, has dynamic properties. This course conducts an in-depth examination of the problems of innovative management that has such dynamic properties. From the inclusive viewpoint of innovative management, the course pays special attention to innovative management by integrating three parts of innovation management: technology innovation, organization innovation, and market innovation. | Elective Core | '4-2 |
| TECHNOLOGY AND STRATEGY | This course teaches technology and strategy as a core aspect of strategic management. After examining the importance of technologic strategy as well as the relation between technological strategy and business strategy, the course teaches technological environment assessment based on the systematic understanding of technological strategy, establishment of methods, execution, evaluation, and control issues of technological strategy. | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT | Financial decision-making in corporations and analytical techniques for solving financial problems are examined in this course. Financial decisions such as investing in fixed assets, obtaining debt and equity funds, and determining the proper amount of working capital are considered. Problems and cases are used to demonstrate the applicability of the analytical techniques. This course also covers the theory and quantitative tools that are necessary for evaluating firm values and understanding financial markets. Specifically, we deal with the valuation of future cash flows, pricing stocks and bonds, capital budgeting, risk and return, and long-term financing. | Required Core | '2-1,2 |
| INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT | This course teaches the characteristics and development trends of information technology as well as the successful management of IT-based firms. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
| MARKETING | The process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services is discussed. The main topics are product, price, place, promotion, marketing planning, organizing, controling, etc. | Required Core | '2-1 |
| CUSTOMER DATA ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT(CAPSTONE DESIGN) | In a rapidly-changing technological environment, it is critical for companies to minimize the perception gap between new product developers and customers in order to reduce market uncertainty. This course focuses on the practical aspects of customer relationship management including how to develop and retain customers and to manage customer information databases effectively. In this course, students will learn the process of NPD (New Product Development) and marketing based on analysis of customer information and surveys by using the statistical software, STATA. The STATA program offers a comprehensive customer analytical tools. With this program, students can conduct powerful analysis and establish practical marketing strategies in order to capture customer value of convergence technologies. | Elective Core | '4-1 |
| MANAGEMENT OF TECHNOLOGICAL KNOWLEDGE AND INNOVATION | This course is designed to provide students with a core knowledge of theories and models of technological innovation. In this process, the subject of technology management is approached as a strategic process for business growth. This course starts with an understanding of the source, type and pattern of innovation, the development of a technological innovation strategy, and the implementation of a strategy. This course is designed for students who are interested in technology innovation management as a major in business administration, or as an engineering student who wants to know how to use their technical knowledge as a manager. In addition, this course reflects the purpose of expanding theory-centered knowledge through the use of related company cases presented in the Harvard Business Review and other sources in parallel with the contents of standard textbooks on technological innovation. There are no special prerequisites that are necessary for this course. Attendance and active participation in class are important, however, and it is essential to have basic competence in reading and understanding materials written in English. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
| BUSINESS AND TECHNOLOGY VALUATION | The accurate and reliable valuation of convergence technologies can provide important information for decision making on R&D investments, technology transactions, and technology strategies. With technology valuation, the investment of ventures and start-ups as well as technology commercialization can be enhanced. This course illustrates the fundamental concepts of valuing convergence technologies or businesses and the valuation process to analyze a business's relative value. It focuses on the different techniques that can be deployed in assessing convergence technology companies. This course provides students with practical problem-solving experiences in evaluating technology-oriented companies. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
| CAREER SUCCESS PROGRAM | Career Success Program is a course for freshmen in the spring semester. The objective of this class is to find each student's talent early and to prepare them for getting their proper jobs after graduation through a tutoring system with professors in the department. | Required Basic | '1-1 |
| CONVERGENCE MARKETING STRATEGY | Convergence Service Marketing Strategy pursues consumer-oriented optimal service creation so that students learn how to maximize consumer satisfaction and utility through the convergence of product and service technology. In order to fulfill such a mission, the class will attempt to broaden topic areas and cover highly advanced or deepened convergence marketing where complicated personal devices with contents embedded and convergent wired or wireless services are provided. Market case study-related research, real market implications, and application tools will also be dealt with in this course. | Elective Core | '4-1 |
| R&D MANAGEMENT | This course teaches efficient management plans of the research and development process, a key area in technology management. The course discusses fundamental theories and examples of R&D strategy, R&D process management, R&D organization, R&D resource control, and business practices of current R&D management. | Elective Core | '2-2 |
| QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN BUSINESS | This course covers quantitative methods for real world business decision-making problems. The quantitative methods and models are based on mathematics, statistics, and systems theory. MS-Excel is used as an educational tool for calculation, interpretation and sensitivity analysis. Topics include mathematical optimization techniques, decision science and deterministic models. This course is closely related to Production and Operations Management, Service Management, and Production and Operation Strategy courses. Basic knowledge of algebra, calculus and statistics is required to take this course. | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| CULTURE, TECHNOLOGY AND CONTENT BUSINESS(CAPSTONE DESIGN) | The cultural content industry has been growing due to the development and diffusion of digital network technology. With the emergence and development of innovative technologies such as smart devices, stabilization technologies of platforms, VR and AI, the market value of the content industry has been rapidly growing. In this evolving and growing cultural content industry and technology, it is critical for the government and companies to create and to manage contents that people can use while generating economic value. This program presents in-depth challenges that extend from content creation to market dynamics, capturing market value, and technology evolution. Moreover, it provides practical educational experiences by analyzing the culture industry including market and technology trends to develop innovative and powerful business strategies. | Elective Core | '4-2 |
| TECHNOLOGY TREND ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING | This course will give students the insights of technology trend analysis and forecasting by providing the chance to study the theoretical backgrounds of technology forecasting and to apply them to practical and real market situations for trend analysis. | Elective Core | '2-1 |
| BUSINESS ENGLISH 1 | The primary objective of this course is to cultivate communication, persuasion and negotiation skills in English. This course will focus on cultivating emotional intelligence, persuasion, and negotiation skills. To the extent possible, students will engage in role plays, active discussions, debates and teams to analyze and solve issues and learn to creatively solve problems. Mid-term will be a case study to increase business acumen. | Basic | '1-1,2 |
| TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT | The course offers a systematic overview of the strategic management plan for key technologies that help improve both businesses and countries' competitiveness in the 21st knowledge-based society. It aims at offering undergraduate students a general understanding on technology management so that they can learn about issues in technology management at corporate and national levels. | Basic | '1-1 |
| ENTREPRENEURSHIP AND VENTURE TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT | Based on the overall contents of start-up and venture management, understanding of entrepreneurship, and management of technology, students will study the theories and case studies of technological management in start-ups and ventures. They can derive solutions to solve the problems and challenges faced by start-ups in the megatrends and management of technology. In this course, teams will be organized to study the cases of other start-ups and venture companies. Presentations follow after studies. Communication and self-directed learning skills will be improved. At the end of the semester, students cultivate not only theories but also practical ability in start-ups and ventures by drawing on these creative skills and challenging practical topics. | Required Core | '3-1 |
| THEORY OF CORPORATE FINANCE | The aim of this course is to acquire basic knowledge required of financial officers and to understand tasks of financial officers. Financial management, an introductory course of finance, deals with valuation methods and their application to the valuation of stocks, bonds, and investment projects. Based on the reading materials that are covered in Financial Management, we study theories and cases that are related to financial decisions of corporations such as finance of capital, capital structure decisions, payout policies, M&A, working capital management, and long-term and short-term financial planning. | Elective Core | '2-2 |
| PRACTICUM AND SEMINAR IN MOT | This course covers recent trends in technology management. Particularly, the course provides students with the opportunity to experience global technology management by holding seminars in technology and management, which focus on representative cases of domestic and foreign technology management. | Elective Core | '4-2 |
| MANAGEMENT OF TECHNOLOGY STANDARD | Technology standards are the key factor for winning in the market. In particular, in the high technology industry, there has been a lot of competition for securing technology standards. Better technologies are not always winning in the market because technology standards have become more important. There have been lots of cases of success and failure in technology standards in diverse industries. Therefore many companies and governments have been trying to formulate and implement standards in many important technologies. For this reason, the efficient management of technology standards is very important in technology management and policy. In this course, students will learn the concept and importance of technology standards, how to manage them, and several important cases of technology standards. | Elective Core | '4-2 |
| INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 1 | Intermediate Accounting I is the first course in the financial accounting sequence. Together with Intermediate Accounting II, this course provides the core of financial reporting knowledge that you will use throughout your academic and professional accounting careers. In addition, this course is designed to assist students in developing critical thinking skills through quantitative and qualitative problem-solving. Topics coverd in this course include financial reporting and accounting ctandards, conceptual framework for financial reporting, income statement and related information, statement of financial position and statement of cash flows, accounting and the time value of money, cash and receivables, valuation of inventories, cost-basis approach, inventories, additional valuation issues, acquisition and disposition of property, plant, and equipment, depreciation, impairments, depletion, and intangible assets. Prerequisite: Principles of Accounting. | Required Core | '2-1,2 |
| NEGOTIATION AND COMMUNICATION | Negotiation is the art and science of generating agreements between two or more parties who have different interests and ideas on bargaining issues. Negotiation is an essential part of business and our everyday lives and negotiation skills are one of the most important requirements for managers who need to handle and control differences between individuals/organizations. This course is designed to help students understand the theories and processes of negotiations so that they can negotiate effectively in a variety of settings. During this course, students will also learn persuasive communication skills, a crucial part of effective negotiation abilities. This course will involve various teaching methods such as lectures, discussions, negotiation exercises, and case studies. | Elective Core | '4-2 |
| BUSINESS STATISTICS | This course introduces basic statistical concepts including descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. For descriptive statistics, we cover data defining and collection, organizing and visualizing data, numerical description, basic probability theory, and some probability distributions. For inferential statistics, we cover sampling theory, estimation, hypothesis testing, one-sample test, two-sample test, analysis of variance, chi-square test, simple regression, multiple regression and so on. Also, students can understand how to use statistical tools such as Excel or R to solve basic statistical problems. | Basic | '1-2 |
| DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION & MANAGEMENT | The purpose of this lecture is to understand the changes of individual, society, and private and public organizations due to IT (Information Technology) enhancement. Students will learn how to utilize IT to add value to corporate business activities and performance. This lecture is the basic course to understand advanced MIS (Management Inforamation System) courses. | Basic | '1-1,2 |
| INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY ANALYTICS | For technology-oriented companies, management of intellectual property has become top priority for survival. Patent landscape analysis is the most important tool, providing insight into the innovations as well as the legal barriers that underlie technology and products. A completed patent landscape analysis project consists of a set of technical references and accompanying analytics from which important legal, business, and technology information can be extracted. This information enables large corporations, startups, universities, research institutions, and investors to understand and make informed decisions prior to investing time and money into new technology and product development opportunities. This course introduces the range of concepts of intellectual property. In particular, patent landscape analysis will be studied in-depth, covering data collection, analysis and visualization. | Elective Core | '2-2 |
| BUSINESS ANALYTICS(CAPSTONE DESIGN) | In today’s competitive environment, it is important to understand the relationships among different business elements, to forecast trends, to recognize the risks arising from management actions, and to optimize investment strategies. Business analytics can be viewed as a process that collects and analyzes huge business data to make an optimal decision. This course aims to improve students’ ability to apply recent business analytic techniques by studying basic theories and analysis tools such as R. This course focuses on application of business analytic techniques rather than fully understanding underlying theories, and is multidisciplinary with links to marketing, finance, operations management, etc. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
| BUSINESS MATHEMATICS | The goal of this class is to teach the basic theory of mathematics and to learn its principles naturally in the course of solving practical economic, management and financial problems. Furthermore, it is necessary to develop the ability to solve problems occurring in actual industrial sites, future risk management, and especially understanding and problem-solving capabilities of financial problems. What is covered in this class will cultivate the necessary mathematical skills in business administration or economics, including : set theory, matrices, functions and limit values, derivatives, integrals, linear transformation, differential equations, multivariate optimization problems, and vector space. | Basic | '1-1,2 |
| PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS | This course aims to deliver fundamental economic concepts to College of Business students so that they will be able to understand basic economic actitivies at consumer, corporate, national and international levels. Students who want to concentrate in finance, accounting, or marketing will find this course encompassing basic elements suitable for upper-level classes. | Basic | '1-1,2 |
| DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL STRATEGY | This course deals with special marketing strategy issues and principles of marketing channel management that have not yet been covered in other marketing related courses. Students will be given the chance to acquire the set of skills required to build and manage the framework for marketing strategy from a firm’s channel manager perspective. Through thorough practice and lecture, students will be well equipped to handle the problems that might arise in their future career as a channel manager. Students will be expected to have prior knowledge regarding retailing, whole selling, and logistics to fully comprehend the designed course. | Elective Core | '4-1 |
| INNOVATIVE MARKETING SOLUTION(CAPSTONE DESIGN) | Innovative Marketing Solution is designed for advanced business students to further their marketing knowledge and skills. This course covers the integration of marketing principles and applies them to the development of a project for a real client’s marketing problem in a digital transformation period. It also develops a deeper understanding of market research; market segmentation; buyer behavior; product development; and the development of marketing mix (4Ps) strategies for both goods and services. It further develops an understanding of the overall process of marketing planning, implementation and control in the contemporary business environment. Students will work in small groups to develop and present a comprehensive marketing strategy based on client goals, research, strategic analysis, and constraints. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
| BUSINESS LAW | Business Law consists of many different areas including contracts, the law of corporations and other business organizations, securities law, intellectual property, antitrust, secured transactions and bankruptcy. This course may deal with capital market related regulations that affect the operation of a business. The purpose of this course is to understand the basic framework of legal relations surrounding enterprises and to cultivate the ability to solve legal problems related to business management. | Elective Core | '2-2 |
| DATA MINING | Data mining, or big data analysis, is the process of analyzing data from different perspectives and summarizing it into useful information - information that can be used to increase revenue, cuts costs, or both. Data mining software is one of a number of analytical tools for analyzing data. It allows users to analyze data from many different dimensions or angles, categorize it, and summarize the relationships identified. Technically, data mining is the process of finding correlations or patterns among dozens of fields in large relational databases. If big data technology is developed in terms of computer engineering, big data analysis is the field of application of business administration and sociology. In this class, the basic concepts of data analysis, as well as the basic algorithms used in data analysis, are taught to understand the principles of data analysis. In addition, we will also practice big data analysis using these principles. In the case of a practice, an offline supplementary course is also provided. | Elective Core | '3-1,2 |
| IT RESOURCE MANAGEMENT AND INNOVATION | IT is the course to enable students to understand the paradigm of IT resource management technologies and skills such as client/server, cloud computing, and outsourcing & utility computing. The newest experiences will be instructed to students utilizing case studies, guest lecturers, or field studies. This course will expose students to managerial issues of information goods or resources, services and enterprise-wide innovations using IT technologies. | Elective Core | '4-2 |
| PRACTICE IN START UP AND 3D PRINTING | This course offers many opportunities and practices in new businesses. Types of new businesses include: one-person companies, home-based businesses, family enterprise start-ups, service start-ups, female-owned businesses, e-business start-ups, high-tech business start-ups, social enterprises, etc. In addition, launching a variety of new products with 3D printing is expected in this course. Using the HCD (Human-centered Design) Toolkit developed by global design company IDEO, we encourage participation in the competition through the stages of idea generation, prototyping, and business plans. Start-up training to experience and evaluate the whole process of a startup follows. Through this, students can communicate effectively with each other and draw cooperation among team members. They can understand various types of information and knowledge, and identify and analyze problems. In the end, they present a solution. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
| TECHNOLOGY COMMERCIALIZATION STRATEGY | The course is aiming at enabling students to develop a conceptual foundation of technology commercialization strategy. It introduces concepts, frameworks and tools for analyzing how firms can commercialize technology based products and services. This course is designed for undergraduate students who want to understand decision making and processes of innovation for technology commercialization. This course deals with most issues related to technology commercialization of the firms, therefore, the concepts, frameworks and tools are useful and relevant when one needs to apply them to real technology commercialization situations. | Elective Core | '4-1 |
| TECHNOLOGY CHARACTERISTICS AND CONVERGENCE | The 21st century has been called the age of convergence. New technologies are emerging as a result of technology convergence. In the age of technology convergence, firms and nations should understand technology convergence and work to manage it. Therefore, this course will teach the meaning, current trends, and future direction of technology convergence. In addition, we will analyze and discuss major cases of technology convergence. | Elective Core | '2-2 |
| MANAGEMENT OF PRODUCT INNOVATION PROCESS IN THE AGE OF FOURTH INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION(CAPSTONE DESIGN) | Learn the product innovation solution process of a global leading company under digital transformation in the fourth industrial revolution and learn technology innovation management issues relevant to strategy and organisation. | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| MARKET RESEARCH IN TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT | This course provides introduction to market research methods in Management of Technology which covers the following broad topics in the market research process: problem definition, research design, data collection methods, questionnaire design, sampling schemes, and data analysis. This course is aimed at the manager who is responsible for determining the scope and direction of market research. Emphasis will be on the use and interpretation of results rather than mathematical derivations. Topics include different types of design, experimental, quasi-experimental design, contingency-table analysis, t-test, ANOVA, and regression. Empirical examples from the field of Management of Techology will be used to illustrate the material covered. By the end of the course, you will be able to design research, organize surveys, analyze data, as well as summarize and report the implications of the results. | Elective Core | '2-2 |
| OPEN INNOVATION | In this course, we focus on the role of open innovation in new product development. We introduce key concepts, forms, and challenges in open innovation and discuss relevant cases studies. Topics include crowdsourcing, innovation from lead users and communities, and open sources that are used in the innovation process. Specifically, students will learn about: 1) the emergence of open innovation and how open innovation differs from other sources of external innovation; 2) the different types of open innovation tools such as crowdsourcing, lead users, innovation intermediaries, and open sources; 3) explore cases of corporations that use open business models and compare them with traditional business approaches; and 4) the challenges of implementing open innovation. | Elective Core | '2-1 |
| ENVIRONMENTAL ANALYSIS | For the effective strategic management of firms, it is critical for managers to equip themselves with skills in analyzing and understanding firms' external and internal environments. Accordingly, Environmental Analysis is designed to train business students to conduct environmental analyses more effectively based on theories and cases. | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| SEMINAR IN BUSINESS MODEL INNOVATION(CAPSTONE DESIGN) | The economical paradigm of the global market is creative innovation. The importance of the innovation process is emphasized now more than ever. The innovation of the business model in particular, has changed the elements that form the business model in many aspects to create a differentiated value. For instance, the market oriented business model has been successful in creating numerous success stories. This course emphasizes the necessity of a market oriented business model within the field of Management of Technology and through examples of various types of business model innovation, this course will analyze examples of company value creation and innovation in revenue models based on a company’s value chain and value proposition. | Elective Core | '2-2 |
| BUSINESS ETHICS | This course is concerned with the roles of corporations, their managers, and the ethical problems they face in real management situations. This course introduces what a society expects from its corporations and managers, and how corporations and managers react to the expectations. In addition, issues concerning environmental protection, discrimination based on gender, and dehumanization inside corporations are discussed. As an applied and multidimensional study, the topics of this course include ethical issues in human resources, marketing, accounting, operations, finance, international business, information systems, and technology management. | Required Core | '4-1,2 |
| TAX ACCOUNTING1 | Understanding the mechanism of determining corporate tax burden, one of the important issues in modern society, to understand the scope of gross income and the scope of deductible expenses for calculating corporate taxable income, and the ability to make reasonable management decisions in consideration of corporate tax burden. The main contents of the study are as follows: characteristics of corporate tax; income disposition; constructive dividends; non-inclusion of items in gross income; deemed profits from lease deposits; repudiation of wrongful calculation; business year in which gross income or deductible expenses accure from a transfer, etc.; scope of non-deductible expenses; provisions for payment of interest and losses; calculation of entertainment and contribution limits; inventory and securities; tax adjustments on amortization of property; plants and equipment; and intangible assets. | Elective Core | '2-2 |
| MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS IN PRACTICE | Big data has been called “21st century oil,” but data will become “blood” beyond “oil” in new industries such as autonomous cars, smart cities, telemedicine and smart finance. In other words, data of information will not just be a critical resource, it will be essential to support the new industry itself. Just as there is no oil industry without oil and no electronics industry without electricity, there is no data and no new industry. Oil, coal, nuclear power, etc. can be replaced by other resources, but blood is essential for the survival of the body and soul, and must be created and circulated. So data is not just a good thing for the future, it's essential for new industries to survive. Just as blood doesn't work, new functions will stop if data doesn't work. In other words, autonomous driving of vehicles is impossible if the traffic information of the navigation does not work. In new industries, good blood must circulate evenly throughout the economy. Without access to data, you won't be able to make a business, and you will have to constantly bleed out and import new and huge amounts of data from outside (real-time sharing, real-time trade in & trade on). In the end, whether or not blood flows smoothly throughout the economy is expected to make or break the new industry. First, this blood itself must be stagnant, clean, and unpolluted, and this blood must flow smoothly not only at the heart of the new industry, but at every point involved, from head to fingertips and the tip of the legs. From this point of view, this course is an extension of the contents of Introduction of Management Information Systems, focusing on case studies about the strategic application of data and information technology. First of all, the trend of big data and information technology changes day by day, and the class will be conducted through presentations and discussions on the latest management cases suitable for each subject. The purpose of this class is to classify the latest cases and to build knowledge of corporate management issues that are digitized in reality. | Required Core | '3-1,2 |
| MARKETING | The overall objective of this course is to introduce students to the fundamental principles and concepts of marketing and to provide students a structure for applying marketing in a decision making framework. After completing this marketing course, each student should attain proficiency in the following areas: 1) Understanding marketing concepts and their application to profit-oriented and non-profit oriented organizations; 2) Applying these concepts to the analysis of marketing problems and development of appropriate and creative marketing strategies to solve these problems; 3) Understanding the need for customer orientation in the competitive global business environment; 4) Having an appreciation that marketing is integrated with other functional areas of business; 5) Developing an understanding and acquiring skills in how to successfully design and implement marketing plans and strategies; 6) Understanding the concept of marketing mix and its application in traditional and novel environments characterized by emerging information technologies; 7) Critically evaluating case studies and analyzing case problems. | Required Core | '2-1,2 |
| MARKETING STRATEGY | Marketing Strategy aims to help undergraduate students to acquire the overall knowledge of marketing as a form of strategy. By putting together the marketing-regarded knowledge which has been acquired so far through other marketing courses, students will confirm their roles as marketing managers and put together the meaning of marketing strategy from a strategical perspective. The students who take this course can complete the framework of marketing in ther perspective of strategy. Through this course, students will identify and master strategical perspectives and strategical decision making skills of a marketing strategist as a virtue required to beceome a successful CEO. | Elective Core | '4-2 |
| MANAGEMENT OF TECHNOLOGY | Students learn concepts, framework, methodology and some cases of management of technological innovation. Students learn about the ever-increasing importance of technological innovation in the era of the fourth industrial revolution. Students learn innovation processes, the dynamic pattern of technical change and how to manage innovation processes and set up technology strategy-leveraging dynamic patterns of technical change. Students learn organization issues relevant to product development teams and firm organization. Students will be introduced to basic concepts of the fourth industrial revolution and its impact on the innovation of firms. The contents are based on the textbook by Melissa A. Schilling (2017) Strategic Management of Technological Innovation. | Required Core | '2-1 |
| TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION AND ECONOMY | This course discusses the economics behind innovation and technology using theories of microeconomics and industrial organization. Topics will include economics of the intellectual property protection system, the relationship between market structure and innovation, and the diffusion of technological innovations. There is no prerequisite for this course; however, prior knowledge of the principles of economics and microeconomics will be helpful. Before moving on to specific topics, we will start with a brief overview of theory of the firm, competitive model, and market structure. In addition to the theories, we will discuss short business case studies relevant to the economics of innovation. | Elective Core | '2-1 |
| CONSUMER BEHAVIOR | In this consumer behavior course, students will understand the psychological principles that underlie decision-making of people in general and consumers in particular. Students will learn about concepts such as attention, categorization, hierarchy of needs, attitude formation, choice models, memory, creativity, customer satisfaction, bias in decision making, symbolic decision making, emotional influences, social influences, and self-control. Students then apply these concepts to understand how consumers make decisions in daily life, and how they can influence consumers’ decisions in their favor. Notably, the analysis of consumer behavior will take into important social trends such as information overload, fragmentation of media, and environmental consciousness among consumers. The insights gained from this course will help students both managerially as well as in their personal lives. Managers in every industry need to understand their consumers’ decision making process. This understanding is the first step towards creating a marketing plan (i.e., positioning, product features, advertising, and pricing) that maximizes consumer demand. Similarly, in personal life, students need to understand “consumers” of your ideas such as colleagues, friends, family and significant others. In summary, the principles learnt in this course will help students understand and influence consumer decision-making in both professional as well as personal areas of their life. | Elective Core | '2-2 |
| PRODUCTION & OPERATIONS STRATEGY | This course introduces students to the essential core and most recent information that every manager needs to know about TQM (Total Quality Management) and performance excellence approaches used in the top organizations, typically firms. The course is divided into 3 basic parts. Part 1 will explain the foundation in the principles of quality management. We first introduce the notion of quality, its history and importance, definitions, basic principles, and its impact on competitive advantage and financial return. The role of total quality in all key economic sectors such as manufacturing, service, health care, education, and the not-for-profit sector will be explored. Topics will include: the philosophical perspectives supporting total quality, chiefly those of Deming, Juran, and Crosby; quality management frameworks defined by the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award and the criteria for performance excellence; ISO 9000; and Six Sigma. In Part 2, an organizational view performance excellence as reflected by the Malcolm Baldrige criteria will be discussed in 6 chapters, for each criteria, customer-focus, leadership, strategic planning, workforce management, process management, and also information and knowledge management. In Part 3, tools and techniques to drive and support design, control, and improvement of quality will be covered. | Elective Core | '4-2 |
| HUMAN RESOURCES DEVELOPMENT | This course is designed to provide an introduction and overview to Human Resource Development. Through this course, students should be able to: 1) understand the importance of training and development for enhanced employee performance and career management; 2) learn how to assess educational and developmental needs of employees and organizations; and 3) know how to plan, design/develop, implement, and evaluate training programs. In addition, a strategic HRD focus on the organization and implementation of HRD initiatives that develop human capital resources for advancing organization's biz strategies and contributing to the organization’s sustainability will be discussed. Through traditional lectures, students will learn major theories related to HRD functions such as learning theories, the concept of transfer of training, ISD model, and Kirkpatrick's 5-level framework drawing from the fields of psychology and education. Also, students will participate in action learning projects where students engage in the actual process of designing a training program on their own. This class will provide students with the conceptual skills, knowledge, and valuable hands-on experiences to understand the functions of HRD and the role of HRD professionals. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
| HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT | In a knowledge-driven global economy, organizations and managers have increasingly recognized that a critical source of competitive advantage often stems not from having the most ingenious product design, the best marketing strategy, or the most state-of-art production technology, but rather from having an effective human resource system for obtaining, mobilizing, and managing the organization’s human resources. Indeed, some scholars and practicing managers contend that in today’s economy with such open access to information, technology, capital, and other resources, effective HRM may be one of the few remaining sustainable sources of competitive advantage. Thus, it is imperative that organizations understand the key HRM functions and how these functions should be aligned in order to gain competitive advantage through their people. This course will provide you with a systematic understanding of HRM. We adopt the perspectives of both general and HR managers. We study the environment of HRM, key HRM functions (e.g., recruitment, training, performance management, compensation), characteristics of effective HRM systems (e.g., strategic alignment of HRM functions, high performance work system), and other important topics such as labor-management issues and international HRM. We will not delve into many technical details of issues relevant only to HR professionals (e.g., all the specifics of job evaluation or the psychometric aspects of test validation). The cases assigned will provide you with the opportunity to test and further develop your ability to identify important concepts regarding HRM in actual organizational settings and to apply these concepts in strategic decision-making. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
| INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 2 | Intermediate Accounting II is the second course in the financial accounting sequence. Together with Intermediate Accounting I, this course provides the core of financial reporting knowledge that you will use throughout your academic and professional accounting careers. In addition, this course is designed to assist students in developing critical thinking skills through quantitative and qualitative problem-solving. Topics coverd in this course include current liabilities, provision, and contingencies, non-current liabilities, equity, dilutive securities and earnings per share, investments, revenue recognition, accounting for income taxes, accounting for pensions and postretirement benefits, accounting for leases, accounting changes and error analysis, statement of cash flows, and presentation and disclosure in financial reporting. Prerequisite: Principles of Accounting & Intermediate Accounting I. | Elective Core | '2-2 |
| ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR | This course is designed to provide an introduction to Organizational Behaviour. We aim to 1) explore individual and organizational factors that have significant impacts on shaping human behavior at work and 2) learn how to effectively manage our own and others’ behaviour. We will pursue these goals using readings, lectures, cases, discussions, experiential exercises, and a team project. | Required Core | '2-1,2 |
| ORGANIZATION DESIGN AND INNOVATION | In a dynamic and turbulent business environment, organizations face myriad management problems. In order to gain and sustain competitive advantage, they should solve these problems successfully. Then, the question is ‘how’ they can solve these problems successfully. Organization Design & Innovation helps organizations, managers, students to figure out how to cope with these problems successfully by providing fundamental knowledge on key topics/points (e.g., aligninng structural dimentions and contextual dimensions, developing organizational strategies and structures, shaping a corporate culture, faciliating organization change and innovation, etc.). This course is relevant to anyone who plans to work within an organization, as career success generally hinges on one’s ability to accurately read and respond to the organizational context within which one operates. The cases assigned will provide students with the opportunity to test and sharpen their ability to identify course concepts in actual organizational settings and to apply these concepts in decision-making. | Elective Core | '3-1 |
| ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR | This course is designed to provide an introduction to Organizational Behaviour. We aim to 1) explore individual and organizational factors that have significant impacts on shaping human behavior at work and 2) learn how to effectively manage our own and others’ behaviour. We will pursue these goals using readings, lectures, cases, discussions, experiential exercises, and a team project. | Required Core | '2-1,2 |
| BASIC PROGRAMMING SKILLS FOR DATA ANALYSIS | Basic programming skills are required for data analysis. Therefore, based on Python, which is currently the fastest growing usage group as a programming language for big data analysis, students learn the basic concepts of computer programming and program basics for data analysis such as data structure. In addition, visualization analysis using Python is dealt with in class, and text mining, analysis and transformation of pictures or photo files are dealt with according to students' program ability. Through this, the goal of this class is to cultivate the ability to use the Python program. | Elective Core | '2-1,2 |
| INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT | This course will cover issues related to both international financial markets and the financial operations of a firm within the international environment. The first part of the course will examine issues related to the international financial markets, including foreign exchange markets, currency derivative markets, and international capital markets. The second part of the course will consider financial issues associated with the operation of a firm in the international environment. Specifically, this part of the course will focus on the identification, measurement, and management of the impact of exchange rates on the firm; issues related to the taxation of international income; firms’ project evaluation, capital structure, and cost of capital for international projects; and financing options and decisions in a global market. While the course examines the theory behind the various issues, it also provides empirical evidence and discussion of firms' real world activities. | Elective Core | '3-2 |
